We had three contestants with four robots:
Author: Albert Diosi

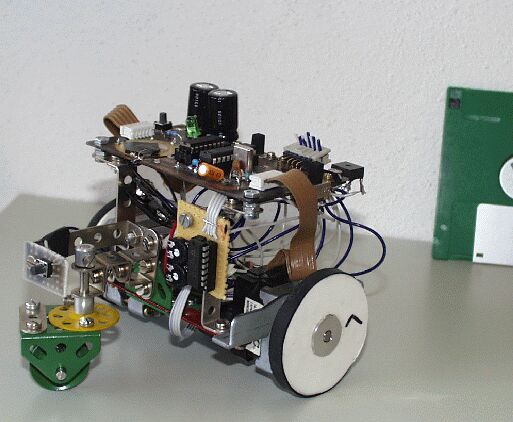
Mobot I. is a three-wheel car with two independent driving wheels and one free-turning support wheel. Car is driven by two stepper motors from an obsolete diskette drive.
Car is controlled by microcontroller Atmel 2051 with darlington array ULN2003.
Senzoric part contains phototransistors illuminated by two red LEDs. Trigger level may be adjusted by trimers.
The robot is powered by usual 1,5 V AA bateries.
Author: Albert Diosi
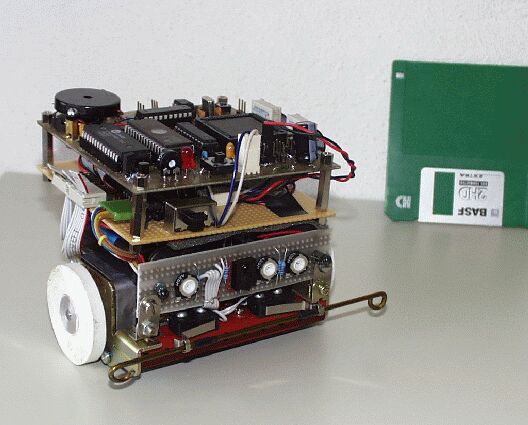
Mobot II. is a mobile robot, based on succesful construction of the Mobot I. Three-wheel car with two independent driven wheels and one free-turning is a more robust construction. Again, wheels are driven by two stepper motors from a 5,25" diskette drive.
Electronics lays on two sandwich boards, powerfull microcontroller Philips 80C552, used for control, is completed with RAM and EPROM.
Sensors are created from photoresistors, illuminated again with red LEDs. Robot is powered from 1,5 V batteries AA type.
Author: Peter Lacko
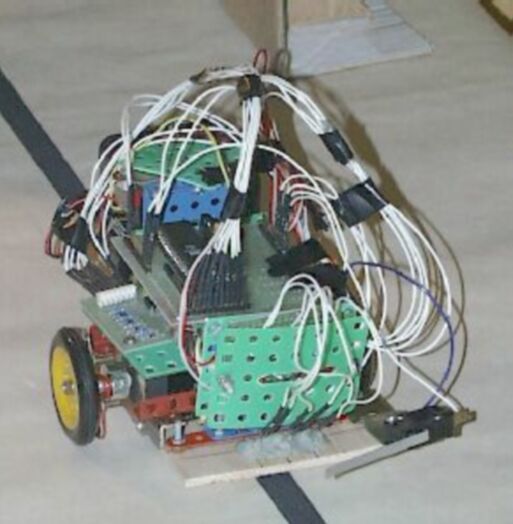
Pathfinder is a simillar construction, three-wheel car driven by stepper motors from diskette drive. Robot contains a high quality wheels from popular children's meccano (construction kit) Merkur. Parts from this kit are used also for hood construction.
Robot is controlled by Atmel 2051 microcontroller with power switch ULN2008.
Front of the robot contains bumper with contact switch to detect obstacles. Robot is powered from set of 1,5 V accumulators.
Author: Jan Palencar
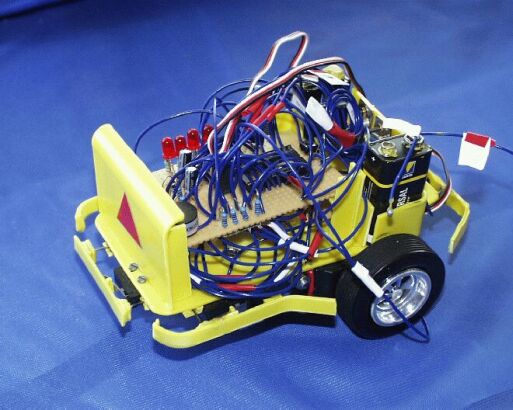

This robot had a very tasteful plastic construction. Again a three-wheel car with two independent wheels driven by Futaba FS100 servos and one free-turning wheel.
Robot was controlled by microcomputer Basic Stamp BSII-SX from Parallax, programmable in language PBASIC. It is a modified version of well-known language BASIC, completed with powerful instructions for I/O ports operation.
Sensors from photoresistors were the weak part of this robot. Failure of one of photoresistors makes the robot unreliable and it was unable to find path in none of the three trials.
Robot was powered from 9 V batteries.